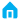
À l'ère de l'Industrie 4.0, les robots industriels sont devenus l'épine dorsale de la fabrication moderne, remodelant les chaînes de production dans tous les secteurs. Des usines d'assemblage automobile aux installations aérospatiales, ces machines programmables ne se contentent pas d'automatiser les tâches, elles révolutionnent l'efficacité, la sécurité et la qualité. Explorons les rôles multiformes des robots industriels et leur impact sur la fabrication mondiale.
1. Fonctions principales des robots industriels
Les robots industriels sont conçus pour effectuer des tâches répétitives, dangereuses ou nécessitant une extrême précision. Leurs applications couvrent les principaux processus de fabrication :
Manutention et palettisation
Les robots excellent dans le déplacement des matières premières, des composants et des produits finis dans les usines. Par exemple, dans les entrepôts de commerce électronique, les bras robotisés équipés de pinces et de systèmes de vision peuvent prélever, trier et emballer les commandes à des vitesses inégalées par le travail humain. Cette automatisation réduit les temps de cycle jusqu'à 50 % et minimise les erreurs dans la gestion des stocks.
Soudure et fabrication
Dans les industries automobile et aérospatiale, les robots effectuent des tâches de soudure de précision telles que le soudage par points, le soudage à l'arc et le soudage au laser. Ces machines garantissent une qualité constante des joints, réduisent le gaspillage de matériaux et fonctionnent dans des environnements avec une chaleur extrême ou des fumées toxiques. Par exemple, un système de soudage robotisé dans une usine automobile peut effectuer 1 200 soudures par heure avec une précision inférieure au millimètre.
Assemblage et démontage
Les robots assemblent des produits complexes tels que des moteurs, des appareils électroniques et des dispositifs médicaux. Les robots collaboratifs (cobots) travaillent aux côtés des humains, gérant des tâches telles que le vissage, l'insertion de composants et le test de cartes de circuits imprimés. Un cobot dans une usine d'électronique peut assembler 500 smartphones par heure avec un taux de défaut inférieur à 0,01 %.
Peinture et revêtement
Les systèmes de peinture automatisés appliquent des couches uniformes de peinture ou de revêtements aux véhicules, aux avions et aux biens de consommation. Ces robots réduisent la pulvérisation excessive de 30 %, garantissant une qualité de finition constante tout en éliminant l'exposition humaine aux composés organiques volatils (COV).
Contrôle qualité
Équipés de caméras haute résolution et de systèmes de vision basés sur l'IA, les robots inspectent les produits pour détecter les défauts. Dans la fabrication de semi-conducteurs, les robots détectent les défauts microscopiques dans les puces avec une précision de 99,9 %, ce qui réduit les taux de rebut et améliore le rendement.
2. Applications spécifiques à l'industrie
Fabrication automobile
Le secteur automobile est le plus grand utilisateur de robots industriels, les utilisant pour :
-
Soudure de carrosserie (BIW): Les robots soudent les châssis de voiture avec précision, assurant l'intégrité structurelle.
-
Ateliers de peinture: Les pulvérisateurs automatisés appliquent la peinture uniformément, réduisant les retouches.
-
Assemblage final: Les robots installent les moteurs, les tableaux de bord et les sièges, réduisant le temps d'assemblage de 40 %.
Aérospatiale et défense
Les robots percent, rivetent et inspectent les composants d'aéronefs, gérant des tâches qui nécessitent des niveaux de tolérance inférieurs à 0,001 pouce. Par exemple, un système de perçage robotisé pour les panneaux de fuselage réduit les erreurs humaines et accélère la production.
Électronique et semi-conducteurs
Dans les environnements de salles blanches, les robots assemblent des micropuces, testent des cartes de circuits imprimés et emballent des composants délicats. Leur précision minimise les risques de décharge électrostatique (ESD), un facteur critique dans la fabrication de semi-conducteurs.
Logistique et entreposage
Les robots mobiles autonomes (AMR) et les bras robotisés optimisent les opérations d'entrepôt en :
-
Prélèvement et emballage: Les robots récupèrent les articles des étagères et les emballent dans des boîtes.
-
Tri: Les robots guidés par la vision trient les colis par destination.
-
Palettisation: Les robots empilent les marchandises sur des palettes pour l'expédition.
3. Avantages des robots industriels
Productivité accrue
Les robots fonctionnent 24 h/24 et 7 j/7 sans pause, ce qui augmente la production. Une usine automobile utilisant des robots peut produire 1 000 véhicules par jour, contre 600 avec le travail manuel.
Sécurité améliorée
En prenant en charge les tâches dangereuses (par exemple, la manipulation de produits chimiques toxiques ou le levage de charges lourdes), les robots réduisent les accidents du travail. Des études montrent une baisse de 70 % des accidents industriels dans les usines adoptant des robots.
Rentabilité
Bien que les investissements initiaux soient élevés, les robots réduisent les coûts de main-d'œuvre de 30 à 50 % au fil du temps. Ils réduisent également le gaspillage de matériaux et la consommation d'énergie, ce qui diminue les dépenses opérationnelles.
Précision et cohérence
Les robots éliminent la variabilité humaine, garantissant que chaque produit répond aux normes de qualité. Dans la fabrication de dispositifs médicaux, cette précision est essentielle à la sécurité des patients.
4. Défis et tendances futures
Complexité de l'intégration
Le déploiement de robots nécessite une expertise en programmation, en étalonnage des capteurs et en intégration des systèmes. Les entreprises s'associent souvent à des fournisseurs de robotique pour une adoption transparente.

 Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères!
Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères! Merci de consulter vos emails!
Merci de consulter vos emails!  Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères!
Votre message doit contenir entre 20 et 3 000 caractères! Merci de consulter vos emails!
Merci de consulter vos emails!